
What happens when a major Ethereum Layer-2 network stops using Etherscan? And that would be the big question after ZKsync officially announced the ZKsync Etherscan Support End, starting January 7, 2026. The move is an important change that is setting in, not merely for users but also for Ethereum's evolving Layer-2 infrastructure.
ZKsync is an Ethereum Layer-2 scaling network. It uses zero-knowledge (ZK) technology to make transactions faster and cheaper while still relying on Ethereum’s security.
Etherscan is a popular blockchain explorer for Ethereum. It lets users check transaction details, wallet balances, smart contracts, gas fees, and block information.
From the said date, "Etherscan will no longer index or support ZKsync Era. Users and developers will be required to move to the native block explorer for transaction and smart contract visibility, as well as on-chain data".
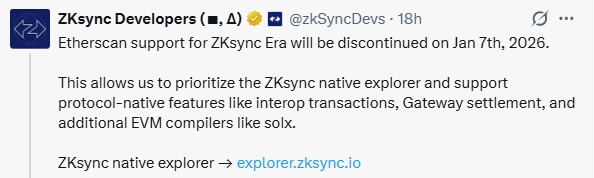
Source: X (formerly Twitter)
The decision behind the ZKsync Etherscan Support End is not sudden. Over time, the zero-knowledge network has grown from a simple Ethereum-compatible chain to a full-fledged network of interconnected chains composed using ZK Stack.
It supports the following advanced features:
Cross-chain and interop transactions
Native settlement via ZKsync Gateway
Compiler support like new LLVM-based Solidity (solx)
These features go beyond the standard set of Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) rules. Therefore, Etherscan can't understand and display-platform's activity. Moreover, it is better for such advanced functions to be clear and accurate in its native explorer.
To everyday users, this means a simple change. Starting January 7, 2026, they will have to use the native explorer to check transactions, wallet balances, or smart contracts.
Developers will be more affected. In general, many applications have utilized the Etherscan API for ZKsync to fetch real-time blockchain data. As the network indexing service ending, all such tools need to migrate to the native explorer API to keep everything working properly.
Due to this change, developers are encouraged to update their bookmarks, dashboards, and analytics tools prior to the deadline, and update their backend systems.
This shows a shift in network's future: Ethereum Layer-2 is becoming more and more independent, professional, and specialized. Advanced networks no longer rely on such shared tools; they need explorers specifically built for their protocols.
This change shows ETH blockchain is moving from a “one-size-fits-all” model into a modular ecosystem. Each Layer-2 now should innovate faster because of less dependency on generic infrastructures.
This, in turn, creates a stronger, more scalable blockchain that is better positioned to deal with mass adoption in the future.
The end of indexing services is not a setback; it's a sign of growth. The path ahead for ZK network has chosen deeper control, better visibility, and long-term scalability.
For users it means a new explorer.
For developers it means migration work.
For ETH Network it means a more mature advanced Layer-2 infrastructure.
January 7, 2026, will become a point where Ethereum scaling networks start building and managing their infrastructures differently.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only, please do your own research before making any investment decisions.

Muskan Sharma is a crypto journalist with 2 years of experience in industry research, finance analysis, and content creation. Skilled in crafting insightful blogs, news articles, and SEO-optimized content. Passionate about delivering accurate, engaging, and timely insights into the evolving crypto landscape. As a crypto journalist at Coin Gabbar, I research and analyze market trends, write news articles, create SEO-optimized content, and deliver accurate, engaging insights on cryptocurrency developments, regulations, and emerging technologies.